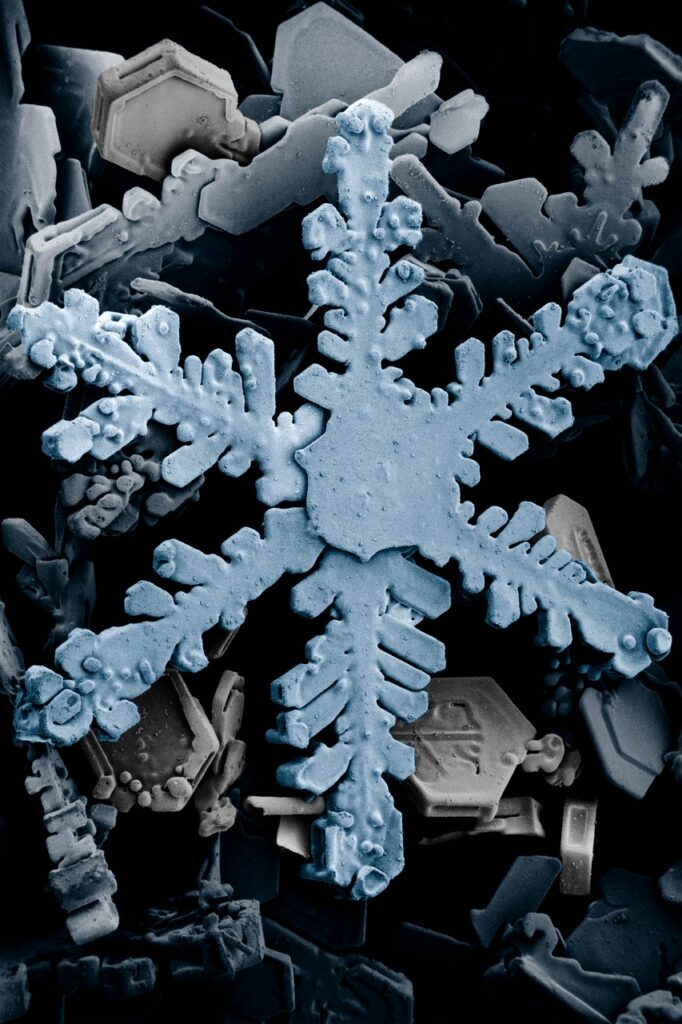
Imagine being able to see a world beyond the naked eye, where tiny objects become larger than life and intricate details come to light. That’s exactly what microscopes offer – an incredible advantage over magnifying glasses. Microscopes open up a whole new dimension of exploration and discovery, allowing you to uncover the fascinating intricacies of the microscopic world. From unraveling the secrets of cells to examining the fine details of ancient artifacts, microscopes provide an unparalleled tool for scientists, researchers, and enthusiasts alike. With their ability to magnify objects to unparalleled levels, microscopes truly unlock a world of wonders waiting to be explored.
Advantages of Microscopes
Microscopes have revolutionized the way we examine the world around us, allowing us to see things in unparalleled detail and clarity. With their ability to greatly magnify and resolve microscopic structures, microscopes offer numerous advantages over traditional magnifying glasses. In this article, we will explore some of the key advantages of using microscopes and their impact on various scientific fields.
Improved Magnification
One of the primary advantages of microscopes is their ability to achieve much higher levels of magnification compared to magnifying glasses. While magnifying glasses typically offer magnification up to 10 times, microscopes can magnify objects up to thousands of times. This improved magnification power enables scientists, researchers, and professionals in various fields to delve deep into the intricate details of the samples they are studying.
Microscopes allow us to observe intricate microscopic structures that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. By magnifying objects to such a high degree, researchers can explore the smallest components of matter, unraveling the mysteries hidden within their complex structures.
Enhanced Resolution
In addition to improved magnification, microscopes offer enhanced resolution, allowing for a clearer and more detailed view of the specimen under examination. The resolving power of a microscope depends on its optical design, with higher-quality microscopes providing superior resolution. This increased resolution helps researchers distinguish smaller details within the sample, leading to a deeper understanding of its structure and composition.
Through enhanced resolution, scientists can identify and study minute features, such as cell organelles, cellular structures, and even nanoparticles. This level of detail is crucial in numerous scientific disciplines, ranging from biology and medicine to materials science and engineering.
Visualization of Microscopic Structures
Microscopes provide a means to visualize microscopic structures that would otherwise remain hidden from our sight. By illuminating the specimen with intense light and using lenses to magnify the image, microscopes make it possible to explore the intricate world of cells, tissues, and other microscopic entities.
The visualization of microscopic structures is vital in fields like biology, where understanding the organization and functioning of cells is fundamental to advancing knowledge in areas such as genetics, physiology, and pathology. Microscopes allow scientists to visually analyze tissues, identify different cell types, study their interactions, and gain a deeper understanding of complex biological processes.
Detailed Examination of Cells
Microscopes play a crucial role in the detailed examination of cells, allowing researchers to study their morphology, structure, and behavior. By using specialized microscopes like fluorescence microscopes, scientists can even observe individual molecules within cells, providing insights into cellular processes at the molecular level.
The detailed examination of cells using microscopes is essential in fields such as medicine and pathology, where the identification and characterization of abnormal cells can aid in the diagnosis of diseases like cancer. By examining cells under a microscope, doctors can detect cellular abnormalities, determine the stage and progression of diseases, and tailor appropriate treatment plans for patients.
Observation of Microorganisms
Microscopes are invaluable tools for the observation of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. These microscopic organisms are often invisible to the naked eye, but microscopes enable us to study their structure, behavior, and interactions.
In fields like microbiology, the observation of microorganisms is crucial for the identification and classification of different species, research on pathogenic microorganisms, and the development of effective treatments. Microscopes allow scientists to analyze the morphology, motility, and growth patterns of microorganisms, leading to a better understanding of their biology.
Study of Organic and Inorganic Materials
Microscopes are not limited to the observation of living organisms; they are also instrumental in the study of both organic and inorganic materials. Whether it is examining the structure of minerals, analyzing the composition of metals, or investigating the properties of polymers, microscopes provide an invaluable tool for material scientists and engineers.
By visualizing the microstructure of materials, researchers can gain insights into their properties at different scales. This information is crucial for developing new materials, understanding material defects and failure mechanisms, and improving the overall performance and functionality of various products.
Identification of Material Composition
Microscopes, particularly advanced types like scanning electron microscopes (SEM) or transmission electron microscopes (TEM), enable scientists to identify the composition of materials with exceptional precision. These microscopes utilize techniques such as X-ray spectroscopy or energy-dispersive X-ray analysis to determine the elements present in a sample.
The ability to identify material composition using microscopes is essential in fields like forensic science, where the analysis of trace evidence plays a crucial role in investigations. Microscopes allow forensic analysts to analyze fibers, gunshot residues, paint particles, and other microscopic evidence, aiding in the identification and linking of materials to specific events or individuals.
Visualization of Nanoparticles
With the advent of nanotechnology, the visualization of nanoparticles has become increasingly important. Nanoparticles possess unique properties and behaviors due to their size, and their observation and characterization require highly specialized tools like electron microscopes.
Microscopes equipped with electron beams, such as scanning electron microscopes and transmission electron microscopes, enable scientists to visualize and examine nanoparticles at the atomic scale. By studying nanoparticles, researchers can understand their properties, behavior, and potential applications in diverse fields such as electronics, medicine, and environmental science.
Observation of Living Organisms
Microscopes offer the invaluable ability to observe and study living organisms in real-time. By incorporating specialized techniques like phase contrast microscopy or confocal microscopy, scientists can observe dynamic processes within living organisms without causing harm or disruption.
The observation of living organisms using microscopes is crucial in various fields, including developmental biology, neuroscience, and ecology. Researchers can track cellular processes, study neuronal activity, and observe the behavior of organisms within their natural habitats, contributing to the understanding of complex biological phenomena.
Contribution to Various Scientific Fields
Microscopes play a central role in advancing knowledge and technological progress across a wide range of scientific fields. From advancing our understanding of fundamental biology to enabling breakthroughs in materials science and nanotechnology, microscopes have contributed significantly to scientific discoveries and innovations.
In medicine, microscopes have revolutionized diagnostics, allowing for early disease detection and precise surgical interventions. In materials science, microscopes have aided in the development of new materials with improved properties. In environmental science, microscopes have facilitated the study of microplastics and their impact on ecosystems.
By enabling researchers to delve into the microscopic world, microscopes continue to drive the progress of scientific knowledge and innovation. Their advantages in magnification, resolution, visualization, and identification of various materials and organisms make them indispensable tools in scientific research, education, and industry.
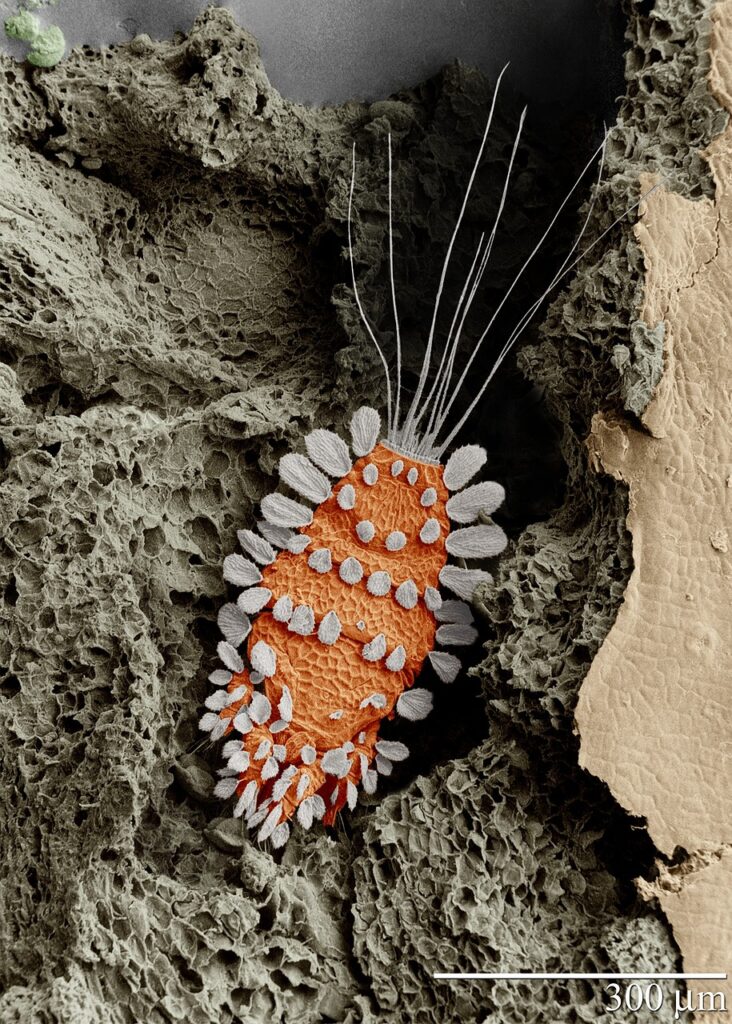
Conclusion
Microscopes offer a multitude of advantages over magnifying glasses, making them indispensable tools in various scientific fields. With their improved magnification and resolution, microscopes allow researchers to explore microscopic structures, examine cells in detail, observe microorganisms, study materials, identify their composition, visualize nanoparticles, and investigate the behavior of living organisms. These advantages contribute to advancements in fields such as biology, medicine, materials science, and nanotechnology. Microscopes continue to push the boundaries of scientific knowledge, enabling breakthroughs and innovations that shape our understanding of the world around us.





